Darzens Epoxide Synthesis
Mechanism + Description
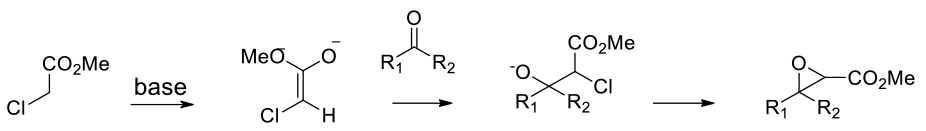
Generation of a carbanion followed by addition to a carbonyl electrophile then intramolecular ring closure
General comments
Aldehydes and ketones condense with a-halo esters in the presence of base to give a,b-epoxy esters (glycidic esters). These may be further hydrolysed to aldehydes and ketones if required. A number of chiral variants have been published. The Darzens reaction may not be suitable if other base sensitive functionality is present. This reaction has been carried out in a wide range of solvents, methanol, toluene, acetonitrile etc.
Key references
Chem. Rev. 55 (2): 283 Mechanisms of The Darzens and Related Condensations
J. Org. Chem. 28 (6): 1514
Green Chem., 2001, 3, 135-136 Darzens in water
Tetrahedron, 1999, 55, 6375-6386 Phase-transfer-catalyzed asymmetric Darzens reaction
Relevant scale up example
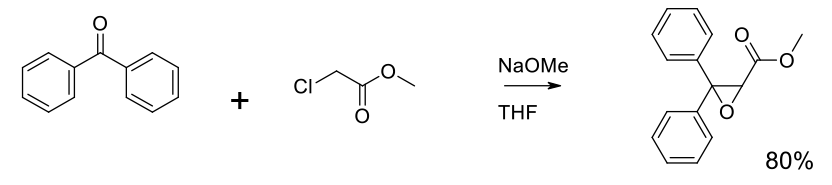
Experimental
180 kg scale
Org. Process Res. Dev. 2001, 5, 16-22
Green Review
-
Atom efficiency (by-products Mwt)
Depends on the reagents used – reasonable atom economy generating a simple inorganic salt and the conjugate acid of the base used – this is the main focus of the mass efficiency of this reaction. - Safety Concerns
No major safety concerns identified. - Toxicity and environmental/aquatic impact
No major issues – impact of solvents used and any by-product from base used would be major areas for concern. - Cost, availability & sustainable feedstocks
Most reagents and bases are cheap and readily available - Sustainable implications
Sodium or potassium alkoxides are preferred to alkyl lithium/ metal amide bases if possible.