Thiols
Mechanism + Description
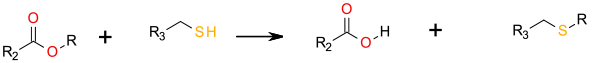
An SN2 mechanism generating the acid and a thio-ether product.
General comments
Sulfur nucleophiles have been used to cleave the carbon-oxygen bond of esters. Thiols have been used in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst, whereas Li and Na thiolates or thiols in the presence of base are reactive without additives. Useful for acid or base sensitive molecules. Examples of esters deprotected include Me, Et, iPr, PhCH2, lactones, 9-anthrylmethyl, phenacyl. KSCN can be used as an inorganic S –based nucleophile.
Key references
Tet. Lett., 2006,47, 565 Triton x405/ KSCN solvent-free dealkylative cleavage of ethers and esters
J. Org. Chem., 2002, 67, 2541 PhSH−(Catalytic) KF in N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone as an Efficient Protocol for Selective Cleavage of Alkyl/Aryl Esters and Aryl Alkyl Ethers
Synthetic Commun., 1975, 5, 305 Cleavage of Methyl and Benzyl Esters by Thiocyanate
J. Org. Chem., 1981, 46, 1991 dealkylation of esters with Al-halide-thiol and Al-halide-sulfide systems
J. Org. Chem., 1986, 51, 3165 SN2-type demethoxycarbonylation of activated esters with 4-aminothiophenol and a caesium catalyst
Relevant scale up example
None found
Green Review
-
Atom efficiency (by-products Mwt)
Depends on the thiol used – low Mwt. preferred, but these give issues with odour. - Safety Concerns
No major safety concerns identified. Many thiols, and to a lesser extent thio ether by-products have odour issues. Many have very low odour thresholds and can be very persistent. Low Mwt . thiols are toxic and highly flammable. - Toxicity and environmental/aquatic impact
No major issues apart from the toxicity of low Mwt thiols. - Cost, availability & sustainable feedstocks
Most thiols are readily available at reasonable cost and generally derived from petrochemical sources. - Sustainable implications
Many of these thiol ester deprotection reactions are conducted in dipolar aprotic solvents, which should be replaced if possible.