Carbon Monoxide / PMC
Mechanism + Description
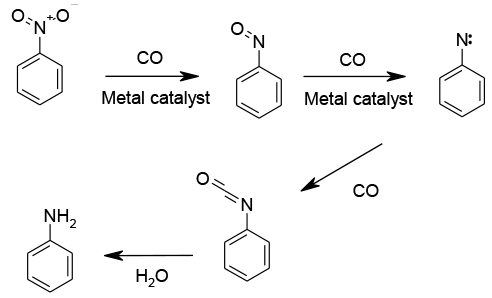
A highly favorable reaction energetically, but as with hydrogenation, it is usuallycatalyzed. The reaction proceeds step-wise viathe nitrosobenzene, Nitrene then isocyante as the primary product. Hydrolysis yields the amine.
General comments
Although CO is a toxic gas, it is industrially very attractive due to its low cost, accessibility, and wide range of applications in the chemical industry. The following review gives an overview of the selective catalytic reduction of aromatic nitro compounds into aromatic amines, isocyanates, carbamates, and ureas using CO. As with hydrogenation, the reaction is very exothermic.
Key references
Chem Rev, 1996, 96, 2035 A Review of the selective catalytic reduction of aromatic nitro compounds into aromatic amines, isocyanates, carbamates, and ureas using CO.
Relevant scale up example
None found.