Pyridines from Biomass
Mechanism + Description
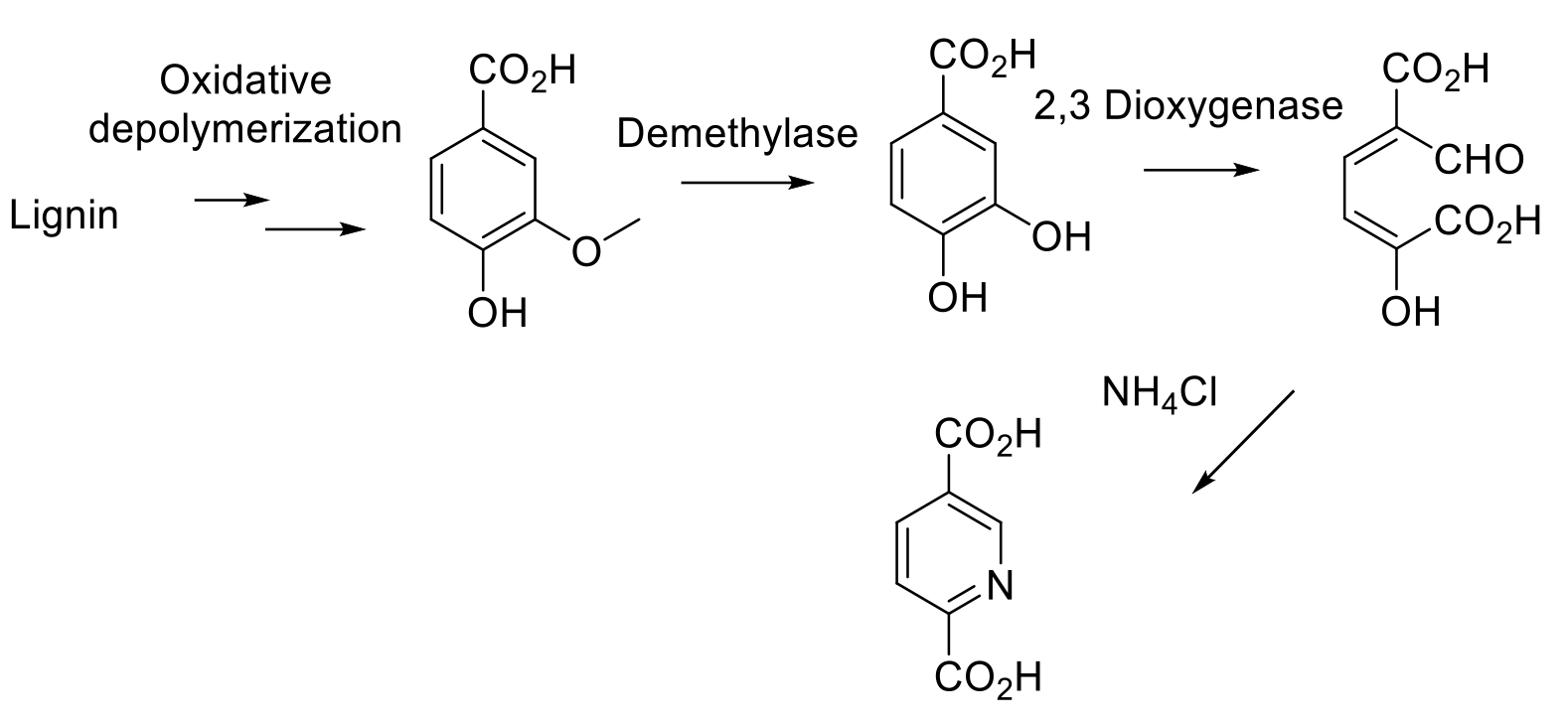
Pyridines from lignin
Aldehydes / ketones in biomass or formed on pyrolysis react with ammonia and aromatize via elimination of oxidation.
General comments
A number of routes have been described that produce pyridines directly from biorenewable feedstocks. Pyrolysis of biomass with ammonia or ammonia derivatives can give pyridines , but synthetic utility is currently somewhat limited by low yields and complex mixtures.
A better strategy toward single pyridine structures is to employ synthetic biology approaches to make single pyridines in a fermentation using modified microorganisms. Routes toward pyridine carboxylic acids using lignin as a feedstock have been described.
Pyridines can be synthesized from furans. A number of these starting materials can be produced from renewable biomass feedstocks like C6 and C5 sugars.
Key references
Scale-up example
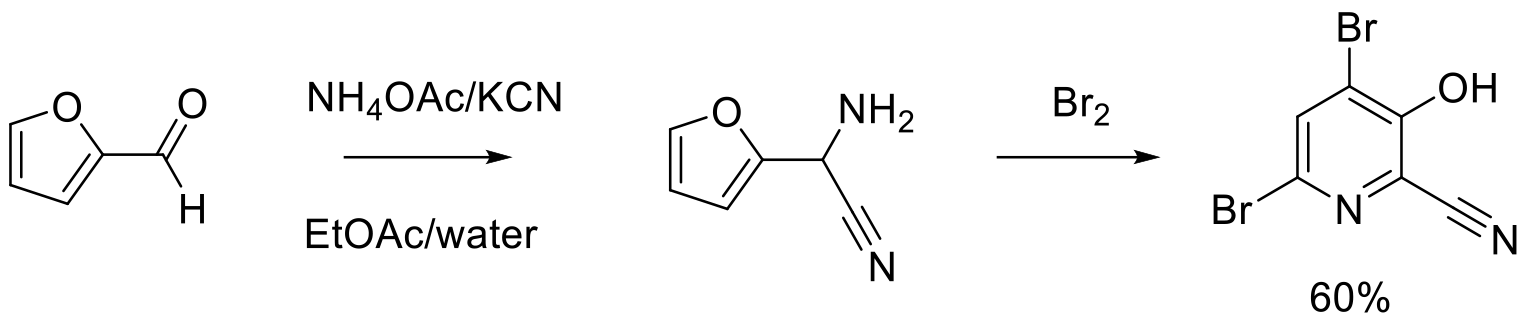
Green Chem. 2020, 22, 6047–6054.
150 g scale