Ishikawa’s Reagent
Mechanism + Description
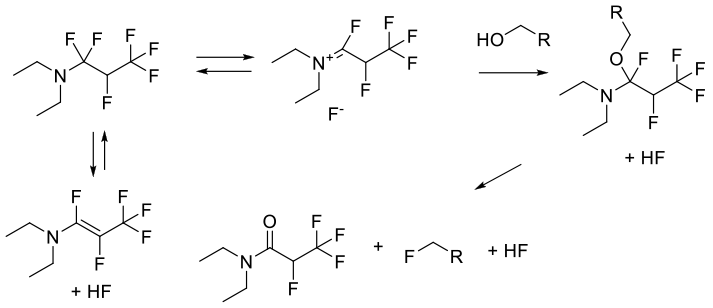
The reagent works by activating the alcohol followed by displacement of the amide-forming leaving group by HF.
General comments
Ishikawa’s reagent (N,N-diethyl-1,1,2,3,3,3-hexafluoropropylamine) is available commercially or often made in situ by condensing perfluoropropene in to a vessel with 1 eq of Et2NH or a higher mol wt secondary amine like piperidine or morpholine. The reagent is used to convert alcohols to fluorides under mild conditions, and often goes with good inversion with chiral alcohols. The reagent is selective for alcohols and does not react with ketones or aldehydes. TFEMDA and Yarovenko’s reagent are related fluorinating agents. Allyl and propagyl alcohols may give rearrangement products.
Key references
Relevant scale up example
None found.