Mechanism + Description
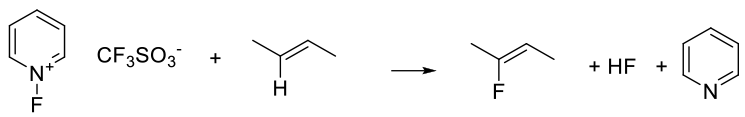
N–F reagents provide a source of F+ and essentially react as electrophilic sources of fluorine reacting with electron-rich unsaturated bonds.
General comments
A range of N centred F+ reagents are available to use in electrophilic fluorination as alternatives to F2. These reagents will attack neutral electron-rich unsaturated bonds. Less reactive centers can be converted to carbanions prior to reaction with the fluorinating agent. N-F reagents can be used in conjunction with Pd catalysis to fluorinate aryl C-H bonds in C-H activation chemistry.
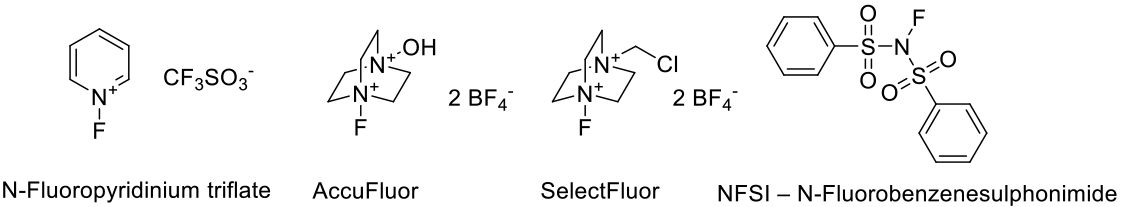
Selectfluor fluorinates a variety of ketones, thioethers, alkenes and aromatic substrates. It can also be used in decarboxylative fluorinations of aliphatic carboxylic acids. Selectfluor may also serve as effective sources of atomic fluorine in the free radical hydrofluorination of unactivated alkenes.
Key references
Lou, S.-J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.-W.; Xu, D.-Q.; He, J.-Q.; Mao, Y.-J.; Xu, Z.-Y. Selective C–H Bond Fluorination of Phenols with a Removable Directing Group: Late-Stage Fluorination of 2-Phenoxyl Nicotinate Derivatives. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2846–2849.
Differding, E.; Ofner, H. N-Fluorobenzenesulfonimide: A Practical Reagent For Electrophilic Fluorinations. Synlett 1991, 3, 187-189.
Umemoto, T.; Kawada, K. Tomita, K. N-FluoropyridiniumTriflate and its Derivatives: Useful Fluorinating Agents. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27, 4465-4468.
Ko, Y.-J.; Park, K.-B.; Shim, S.-B.; Shin, J.-H. Synthesis of DifluorinatedPyridinecarboxaldehyde Via Electrophilic Fluorination. J. Fluor. Chem. 2006, 127, 755-759.
Anbarasan, P.; Neumann, H.; Beller, M. Efficient Synthesis of Aryl Fluorides. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2219-2222.
Umemoto, T.; Tomita, K.; Kawada, K. N-FluoropyridiniumTriflate: An Electrophilic Fluorinating Agent. Org. Synth. 1990, 69, 129.
Stavber, S.; Jereb, M.; Zupan, M. Solvent directing immediate fluorination of aromatic ketones using 1-fluoro-4-hydroxy-1,4-diazoniabicyclo[2.2.2]octane bis(tetrafluoroborate). Chem. Commun. 2000, 14, 1323-1324.
Stavber, G.; Zupan, M.; Jereb, M.; Stavber, S. Selective and Effective Fluorination of Organic Compounds in Water Using Selectfluor F-TEDA-BF4. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 4973–4976.
Stavber, G.; Zupan, M.; Stavber, S. Micellar-System-Mediated Direct Fluorination of Ketones in Water. Synlett 2009, 4, 589-594.
Yin, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, C. Silver-CatalyzedDecarboxylative Fluorination of Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids in Aqueous Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10401-10404.
Barker, T. J.; Boger, D. L. Fe(III)/NaBH4-Mediated Free Radical Hydrofluorination of Unactivated Alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13588-13591.
Banks, R. E.; Mohialdin-Khaffaf, S. N.; Lal, G. S.; Sharif, I.; Syvret, R. G. 1-Alkyl-4-fluoro-1,4-diazoniabicyclo[2.2.2]octane Salts: A Novel Family of Electrophilic Fluorinating Agents. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.1992, 8, 595-596.
Singh, R. P.; Shreeve, J. M. Recent Highlights in Electrophilic Fluorination with 1-Chloromethyl-4-fluoro- 1,4-diazoniabicyclo[2.2.2]octane Bis(tetrafluoroborate). Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 31-44.
Yang, J.-D.; Wang, Y.; Xue, X.-S.; Cheng, J.-P. A Systematic Evaluation of the N-F Bond Strength of Electrophilic N-F Reagents: Hints for Atomic Fluorine Donating Ability. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 4129-4135.
Rozatian, N.; Ashworth, I. W.; Sandford, G.; Hodgson, D. R. W. A Quantitative Reactivity Scale for Electrophilic Fluorinating Reagents. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 8692-8702.
In the presence of chiral ligands/complexes, construction of chiral C-F bonds is feasible:
Suzuki, T.; Goto, T.; Hamashima, T.; Sodeoka, M. Enantioselective Fluorination of tert-Butoxycarbonyl Lactones and Lactams Catalyzed by Chiral Pd(II)-Bisphosphine Complexes. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 246–250.
Lectard, S.; Hamashima, Y.; Sodeoka, M. Recent Advances in Catalytic Enantioselective Fluorination Reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 2708-2732.
Reddy, D. S.; Shibata, N.; Nagai, J.; Nakamura, S.; Toru, T.; Kanemasa, S. Desymmetrization-Like Catalytic Enantioselective Fluorination of Malonates and its Application to Pharmaceutically Attractive Molecules. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 164-168.
Wang, X.; Lan, Q.; Shirakawa, S.; Maruoka, K. Chiral Bifunctional Phase Transfer Catalysts for Asymmetric Fluorination of β-Keto Esters. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 321-323.
Relevant scale up example
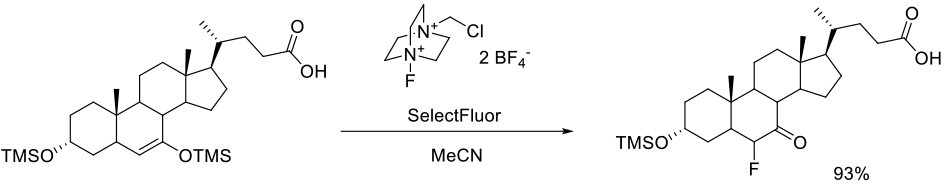
Königsberger, K. Chen, G.-P.; Vivelo, J.; Lee, G.; Fitt, J.; McKenna, J.; Jenson, T.; Prasad, K.; Repič, O. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2002, 6, 665-669.
Experimental
270g scale
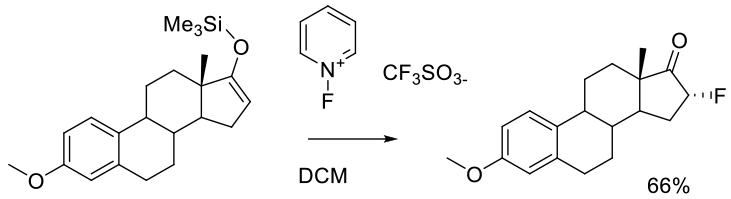
Umemoto, T.; Tomita, K.; Kawada, K. Org. Synth. 1990, 69, 129.
Experimental
7g scale
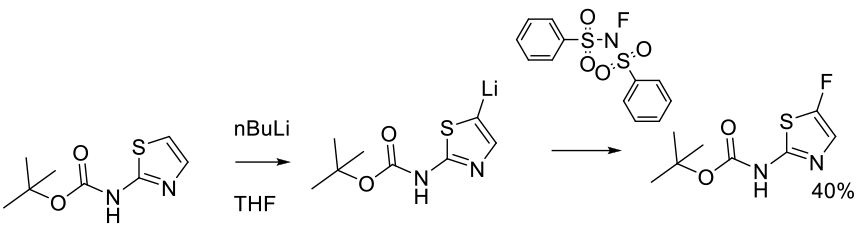
Briner, P. H.; Fyfe, M. C. T.; Martin, P.; Murray, P. J.; Naud, F.; Procter, M. J. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2006, 10, 346-348.
Experimental
1kg scale
Green Review
-
Atom efficiency (by-products Mwt)
Poor atom economy reagents being surrogates for F2. However, being stable crystalline substances they offer reduced reactivity and operational simplicity compared to F2 gas. The byproducts are conjugate acids of the nitrogen base. Fluoropyridinium salts offer the best atom efficiency in this class.
- Safety Concerns
These materials require less specialised handling and containment compared to F2. With these reagents, materials compatibility can be an issue, and these F+ reagents can react violently with certain solvents and other organic materials.
- Toxicity and environmental/aquatic impact
High concentrations are damaging to all lifeforms, but these materials are too reactive to persist in the environment. Any long term issues would reflect the ecotoxicity of the conjugate nitrogen bases and any anions used. Trifluoromethanesulphonate (triflate) is persistent.
- Cost, availability & sustainable feedstocks
Most are available in bulk but are expensive reagents.
- Sustainable implications
These are poor atom efficiency reagents that come from F2. They are high LCI materials.




