Sulfur-Based Fluorinating Agents
Mechanism + Description
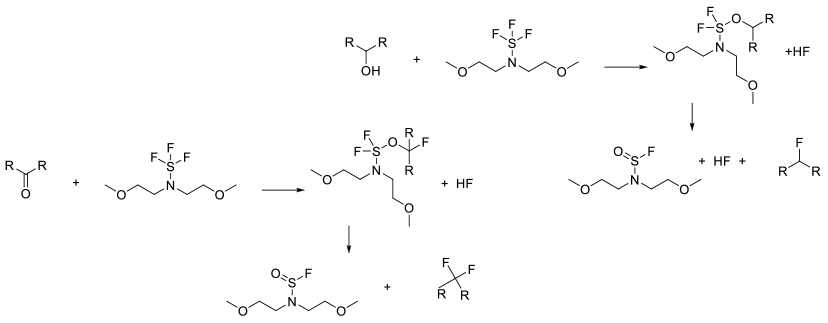
All S-F reagents work by activation of the alcohol/carbonyl followed by reaction with fluoride or HF to give the fluoride plus S=O by products. For alcohols, the final displacement can be SN1 or SN2, so clean inversion is not always seen. Ketones can give vinyl fluorides as by-products.
General comments
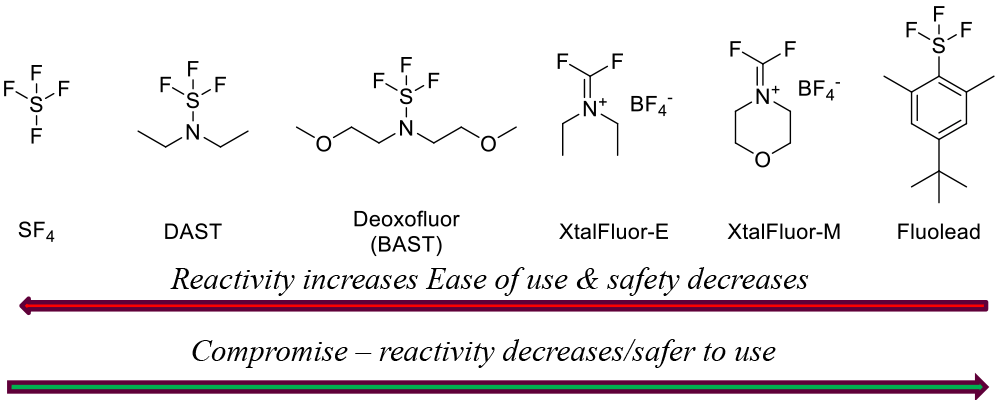
Over a number of years, a family of S-F deoxyfluorination reagents has grown around SF4. SF4 is highly reactive and needs special facilities to handle safely. These reagents convert alcohols to alkyl fluorides and aldehydes/ketones to gem difluorides. Fluorination with reagents like DAST and Deoxofluor can be catalyzed with trace amounts of HF, Lewis acids or silicates.
Hazards with the more reactive S-F reagents can be mitigated somewhat by the use of flow reactors.
Key references
Middleton, W. J.; Bingham, E. M. 4-Nitrobenzyl Fluoride. Org. Synth. 1977, 57, 72.
L’Heureux, A.; Beaulieu, F.; Bennett, C.; Bill, D. R.; Clayton, S.; LaFlamme, F.; Mirmehrabi, M.; Tadayon, S.; Tovell, D.; Couturier, M. Aminodifluorosulfinium Salts: Selective Fluorination Reagents with Enhanced Thermal Stability and Ease of Handling. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 3401–3411. (Note these reagents need either the addition of a base as a promoter or an exogenous source of fluoride.)
Wang, C.-L. J. Fluorination with Sulfur Tetrafluoride. Org. React. 1985, 34, 319-400.
Relevant scale up example
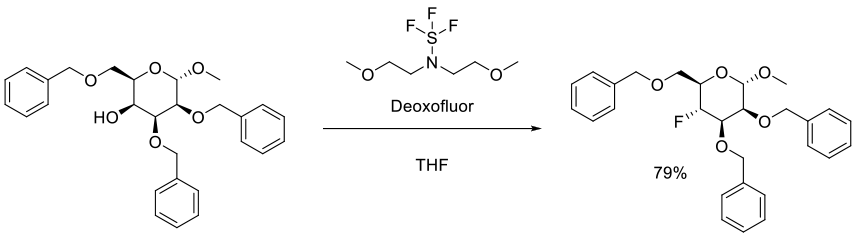
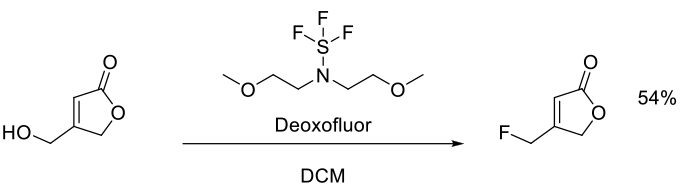
Weiberth, F. J.; Gill, H. S.; Jiang, Y.; Lee, G. E.; Lienard, P.; Pemberton, C.; Powers, M. R.; Subotkowski, W.; Tomasik, W.; Vanasse, B. J.; Yu, Y. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2010, 14, 623–631.
Experimental
115kg scale
Adam, J.-M.; Foricher, J.; Hanlon, S.; Lohri, B.; Moine, G.; Schmid, R.; Weber, M.; Wirz, B.; Zutter, U. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2011,15, 515-526.
Experimental
10kg scale
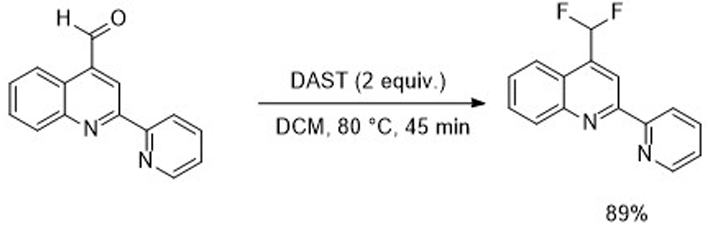
Baumann, M.; Baxendale, I. R.; Martin, L. J.; Ley, S. V. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 6611-6625.
Experimental
<100g scale
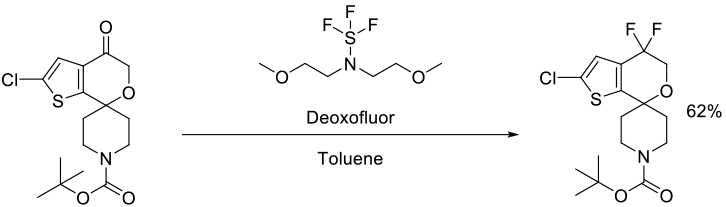
DeBaillie, A. C.; Jones, C. D.; Magnus, N. A.; Mateos, C.; Torrado, J. P.; Wepsiec, J. P.; Tokala, R.; Raje, P. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1568–1575.
Experimental
20kg scale
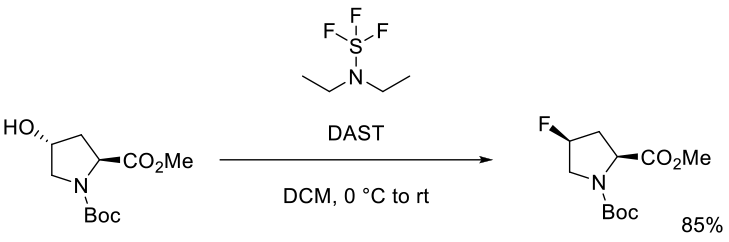
Kim, B. C.; Kim, K.-Y.; Lee, H. B.; Shin, H. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2008, 12, 626–631.
Experimental
3.5kg scale
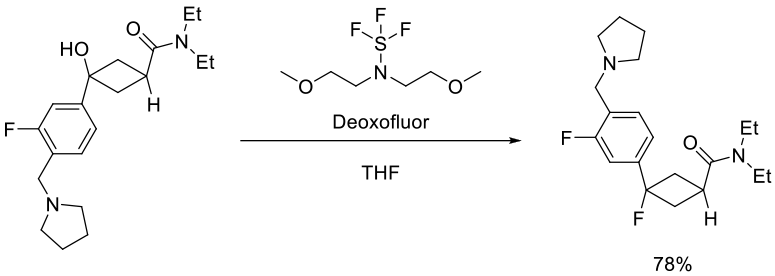
Hawkins, J. M.; Dubé, P.; Maloney, M. T.; Wei, L.; Ewing, M. Chesnut, S. M.; Denette, J. R.; Lillie, B. M.; Vaidyanathan, R. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2012, 16, 1393−1403.
Experimental
35g scale
Green Review
-
Atom efficiency (by-products Mwt)
All are poor atom economy reagents for the introduction of fluorine—better for gem difluorides—but offer increased safety and operational simplicity compared to SF4. Stability increases along the series shown, but this is a trade off vs. reactivity. By-products are SO2, HF and the corresponding amines. - Safety Concerns
Lower MWt. Materials can be explosive and all can react violently with certain solvents and other organic materials liberating HF. DAST is particularly unstable since it can generate SF4 and (Et2N)2SF2 when heated. Since these reagents generate HF during reaction and work-up, safety concerns are as for HF, i.e., severe burns and materials incompatibility. Hazards can be somewhat mitigated by using these reagents in flow systems. - Toxicity and environmental/aquatic impact
Due to high reactivity to water, it is unlikely that these reagents would persist. Issues as for HF. - Cost, availability & sustainable feedstocks
Most are available in bulk but are expensive reagents. - Sustainable implications
These are poor atom efficiency reagents that come from SF4– hence ultimately F2. They are high LCI materials.