Thioalkylation with Sulfur as the Electrophile
Mechanism + Description
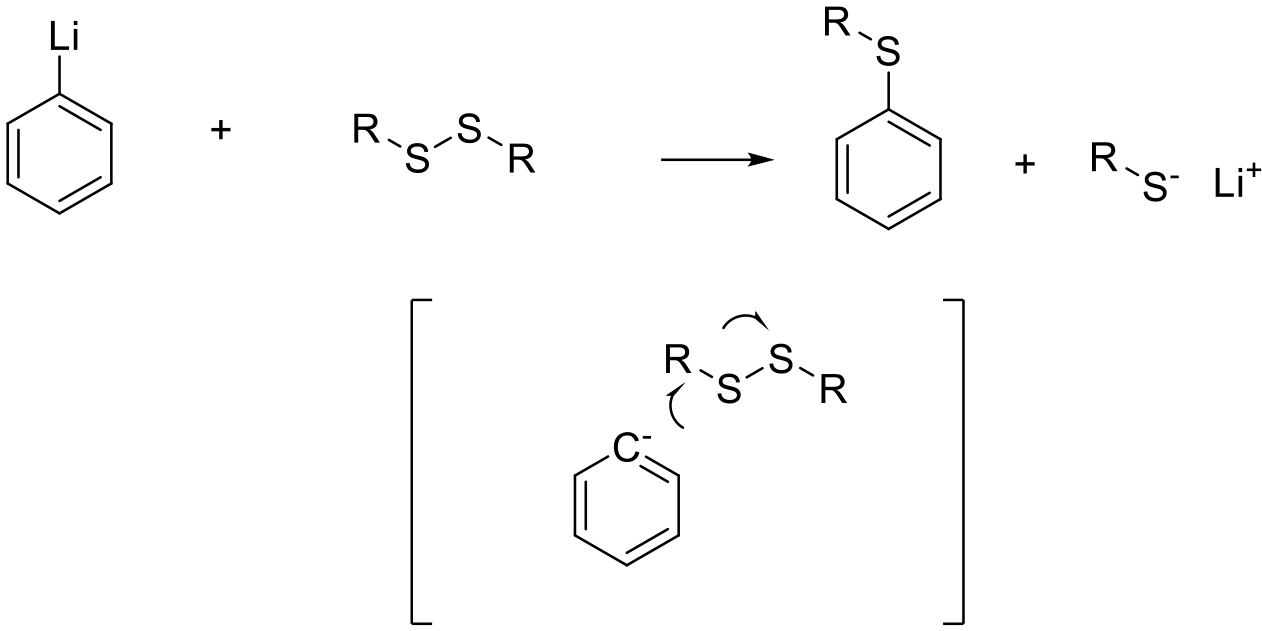
Attack of a carbon nucleophile on a sulfur atom activated by a suitable leaving group generating the thioether.
General comments
Essentially an umpolung of the classical Williamson-type ether synthesis where the sulfur atom is the electrophile and the carbon synthon a nucleophile. Typically the leaving group will be electron withdrawing thus activating sulfur towards nucleophilic attack. A number of leaving groups have been described: symmetrical disulfides, unsymmetrical disulfides where attack at the required S atom can be directed, S-Cl, S-CN, Bunte salts and thiosulfonates. The nucleophile can be an organometallic species, e.g., Li, MgX or an electron-rich arene/heteroarene. In the case of electron-rich aromatics, Lewis acidic metals are often used as catalysts. Recently, disulfides have been described as coupling partners in Pd-catalyzed synthesis of aryl thiol ethers.
Key references
Relevant scale up examples
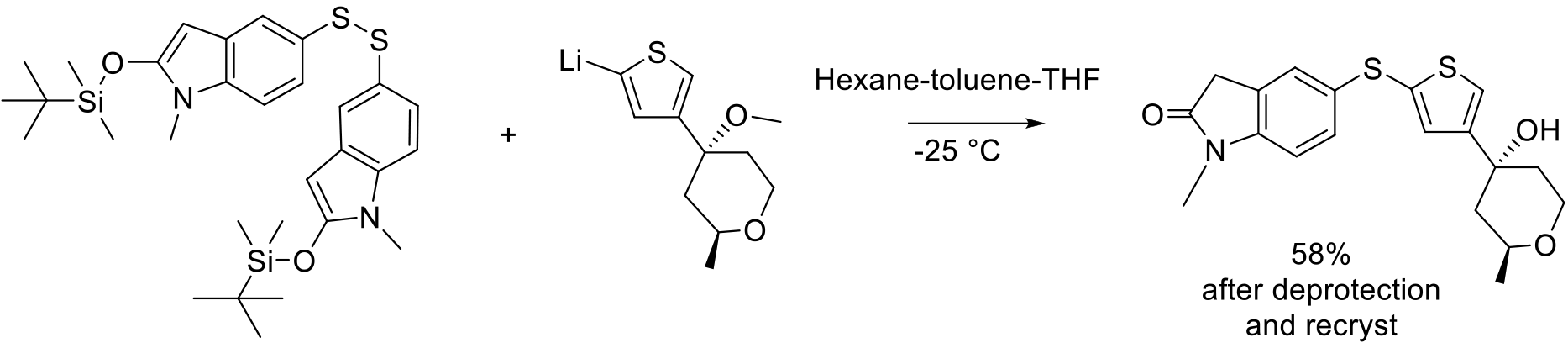
Org. Process Res. Dev. 2005, 9, 555–569
60 kg scale
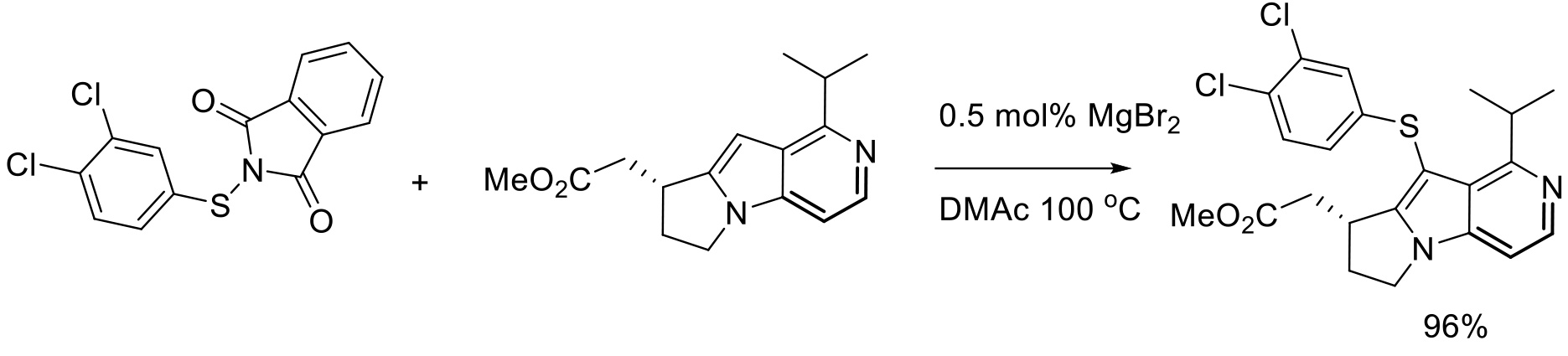
Org. Process Res. Dev. 2010, 14, 787–798.
2 kg scale

Org. Process Res. Dev. 2012, 16,1746−1753.
60 kg scale
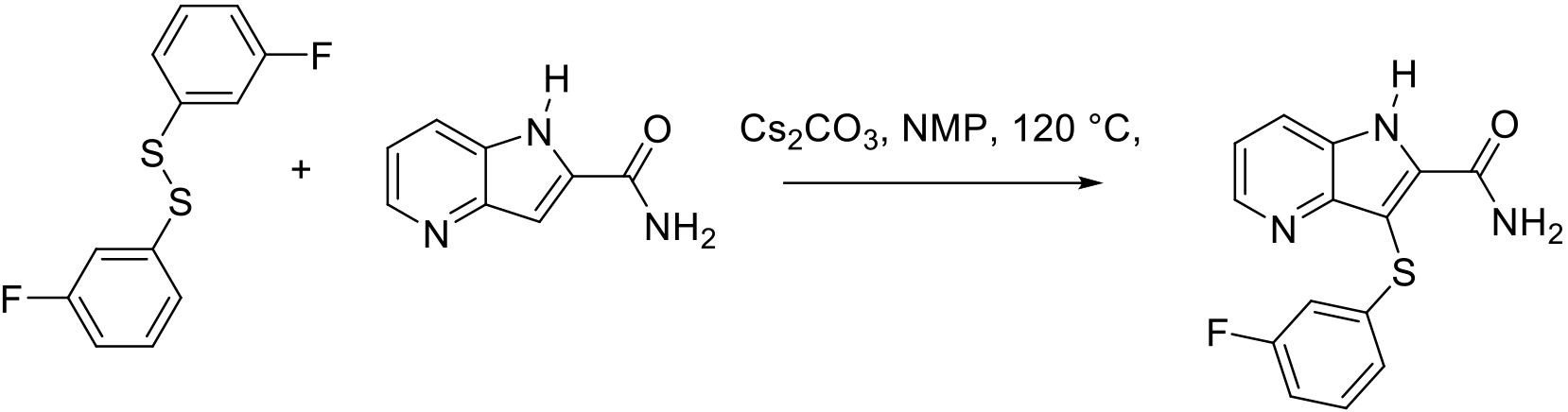
Org. Process Res. Dev. 2011, 15, 1040–1045.
200 g scale