PDC Pyridium Dichromate Oxidations – Cornforth Reagent
Mechanism + Description
Most chromate (VI) reagents work via a common mechanism – formation of a chromate ester followed by oxidative elimination of Cr (IV) and the oxidized alcohol product.

General comments
PDC and the related PCC are among a range of Cr (VI) oxidants available. Other variants exist with modifications like amine ligands etc. Once widely used, there are still recent publications claiming greener and solvent free oxidations with Cr reagents – this said, chromium reagents should almost always be viewed as a less preferred option in terms of green chemistry.
Key references
Luzzio, F. A. The Oxidation of Alcohols by Modified Oxochromium(VI)–Amine Reagents. Organic Reactions. 1998, 53, 1-221. – Review of modified oxochromium (VI)-amine reagents
Muzart, J. Chromium-catalyzed oxidations in organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92 (1), 113-140. – Review of Chromium catalysed oxidations
Relevant scale-up example
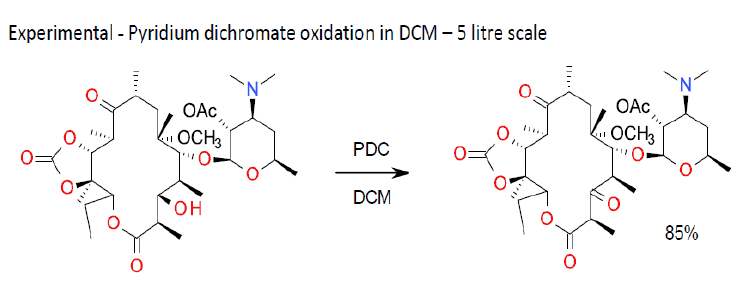
Org. Process Res. Dev. 2006, 10 (3), 446–449.
Green Review
- Atom efficiency (by-products)
Very poor – removal of H2 generates 378 waste - Safety concerns
Chromium (VI) reagents strongly support combustion and can present an explosion hazard in contact with organic materials - Toxicity and environmental/aquatic impact
Chromium (VI) compounds are both acutely toxic (irritant) and known to be carcinogenic to mammals, and are also very hazardous to aquatic organisms. Many Cr (VI) compounds are on the European Union’s REACH Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) list due to their carcinogenic properties. Toxic via skin, ingestion and inhalation - Cost, availability & sustainable feedstocks
Chromium reagents are cheap and readily available, although increasingly stringent legislation may make their use increasingly difficult.
http://echa.europa.eu/candidate-list-table
http://www.epa.gov/ttnatw01/hlthef/chromium.html - Sustainable implications
These reagents often form intractable residues after reaction that can result in protracted cleaning procedures. All metals have a high LCA impact from mining and refining operations, so use should be catalytic with recovery and recycling. Chromium is currently listed as being at low risk of depletion.