TPAP/NMO (tetrapropylammonium perruthenate)
Mechanism + Description
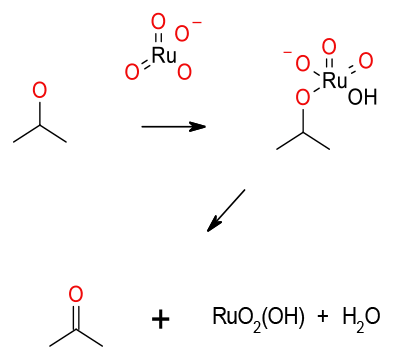 TPAP provides a source of Ru(VII) soluble in a range of organic solvents. Alcohol oxidation is via a Ru complex generating Ru-(V) and the product. The catalyst is regenerated using an added terminal oxidant, usually N-methyl morpholine-N-oxide.
TPAP provides a source of Ru(VII) soluble in a range of organic solvents. Alcohol oxidation is via a Ru complex generating Ru-(V) and the product. The catalyst is regenerated using an added terminal oxidant, usually N-methyl morpholine-N-oxide.
General comments
This is a mild and more easily controlled version of RuO4. The organic salt is soluble in a range of organic solvents. Often used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes, the complex is used catalytically and driven by the addition of a terminal oxidant. The by-product of water needs to be removed to minimize over-oxidation to the acid. The original oxidant, morpholine N-oxide (NMO), gives rise to poor atom economy. Later variants have attempted to address this by using air instead as the co-oxidant.
Key references
Ley, S. V.; Norman, J.; Griffith, W. P.; Marsden, S.P. TPAP: A Catalytic Oxidant for Organic Synthesis. Synthesis. 1994, 639.
Markó, I. E.; Giles, P. R.; Tsukazaki, M.; Chellé-Regnaut, I.; Urch, C. J.; Brown, S. M. Efficient, Aerobic, Ruthenium-Catalyzed Oxidation of Alcohols into Aldehydes and Ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119 (51), 12661-12662.
Wheeler, R. C.; Benali, O.; Deal, M.; Farrant, E.; MacDonald, S. J. F.; Warrington, B. H. Mesoscale Flow Chemistry: A Plug-Flow Approach to Reaction Optimisation. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2007, 11 (4), 704-710.
Relevant scale-up example

Org. Process Res. Dev. 2001, 5 (5), 498–507.
Green Review
- Atom efficiency (by-products)
While it has a high molecular weight, TPAP is catalytic and can usually be optimized to have minimal effect on mass balance. The major atom efficiency hit is from the reoxidant. N-methyl morpholine N-oxide generates a stoichiometric amount of N-methyl morpholine as a by-product. - Safety concerns
The reactions can be quite exothermic and hard to control in some instances. Small-scale observation and assessment is strongly recommended before scale-up. - Toxicity and environmental/aquatic impact
Generally low impact with low catalytic loadings. As with all heavy metals, contamination of the environment needs to be avoided and levels in the final active pharmaceutical ingredient need to be controlled. Other risks depend on the co-oxidant used. - Cost, availability & sustainable feedstocks
Though TPAP is catalytic, it is also expensive with some limitations on scale. - Sustainable implications
Like most precious metals, Ru has a high LCI, and is rated at high risk of depletion.